This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
Read more
NEWS: What’s the Latest in New Drug Discovery in 2023?
June 27, 2023

What's the Latest in New Drug Discovery in 2023?

by Adrienne L. Watson, PhD
Chief Scientific Officer, World Precision Instruments
In 2022, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved 37 new drugs, of which 20 were chemical entities and 17 were biologics.1 In 2023, drug discovery remains strong with many new advancements a result of changing landscapes in both the types of drugs that are being developed and the new and innovative assay that are being launched to evaluate drugs preclinically. Therapeutic development is still highly focused on diseases that affect large populations of people for which there are lack of effective treatments, with 2023’s most anticipated drug launches expected to be in areas of cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, cardiovascular disease, and ulcerative colitis.2
Therapies that are being developed today look much different than the drugs of the past, with a large representation of biologics, cell, and gene therapies. In fact, in 2022, the cell, gene, and RNA pipeline grew from 3,726 therapies in development, a 7% growth over the previous year.3 These advanced therapies have led to an increased need for advanced manufacturing and a growth in synthetic biology. While many of the first cell and gene therapies targeted monogenetic disease, research laboratories and pharmaceutical companies are now tackling more complex diseases, many of which may rely on a combination therapy approach to effectively treat patients. Combination therapies add an additional layer of complexity to both preclinical studies and clinical trial design. Complex diseases, like cancer and neurodegenerative diseases require that patients are treated as individuals, bringing personalized medicine to the forefront of drug discovery and development. We now understand how different two tumors can be, even when they originate from the same organ. For example, two of the same type of brain tumor may be more genetically different than a liver and lung tumor, behave in completely different manners, and therefore, be susceptible to different drugs. Therefore, approaches like genomics, transcriptomics, and AI are critical to delivering the kind of personalized medicine needed to tackle the most aggressive and intractable diseases. This also leads to new ways in which drugs enter clinical trials, with a focus on blood and tissue-based biomarkers for patient-centric clinical trials. Patient-centric clinical trials prioritize the needs of patients at all stages of the trial from trial design to enrollment to outcome reporting and help ensure that the outcomes are relevant and meaningful to patients.4
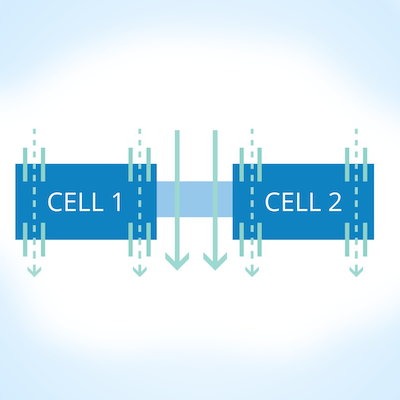
More complex and predictive preclinical assays are being developed to model the intricate and elaborate biology of human organ systems and the pathology that underlies these diseases. But, while modeling complexity is key, 2023 has also seen the passage of the FDA Modernization Act 2.0 that allows for adequate alternatives to animal testing in drug development.5 Therefore, 2023 has seen the rapid expansion and advancement of complex preclinical assay systems such as 3D cell and tissue models and organ-on-a-chip technology, where one can replicate multiple organ systems in a micro-physiological system to understand how a disease works and identify therapeutics that will safely and effectively improve patient outcomes. These eloquent and unique assays have become multidisciplinary, bringing in aspects of immunology, electrophysiology, genetics/gene-editing, physics/fluidics, and automation to develop the ideal preclinical simulations to perform drug discovery on. For example, some of the most complex organ-on-a-chip models bring together a variety of cell types from a given tissue and the microenvironment of that tissue, such as brain endothelial cells, neurons, astrocytes and immune cells such as microglia to model the blood brain barrier or liver chips that include epithelia, endothelia, hepatocytes, stellate cells and immune cells. These micro-physiological systems have microfluidic capabilities that mimic the physiological flow within the human body, exposing cells to biological sheer stress and can even integrate electrophysiological and visual readouts of cell behavior and drug activity, such as transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) to monitor barrier activity and complex microscopy to visualize cell behavior. Further, gene-editing and induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) technologies enable researchers to replicate the genetic changes that underly patient disease in the cells and tissues of these systems to further model a given disease.
As we move towards the end of 2023, we will continue to see a race towards designing the most biologically relevant, complex preclinical systems, with rapid and reproducible readouts of therapeutic safety and efficacy critical for fast and accurate drug discovery. These new preclinical models must be applicable to not only small molecules, but to peptides, antibodies, cell, gene, and RNA therapies that are rapidly advancing from preclinical pipelines and into clinical development. The assays that we deploy in the laboratory must tell us about how biological systems function under normal conditions, disease conditions, and when drugs are given, to accurately predict patient response and to develop biomarkers for therapeutic vulnerability and adverse effects. These systems must read out both safety and efficacy and have the capacity to predict how individuals will respond to a given therapy.
WPI is at the forefront of drug discovery in 2023. We are partnering with research institutions, biotechnology companies, and pharmaceutical laboratories to develop and deploy the instrumentation critical for finding treatments and cures for the disease focus areas of today. WPI offers solutions for cell and tissue biology, fluidics, animal physiology, and electrophysiology. Our focus today is to enable the most rapid and reproducible results from our instrumentation to support innovative and successful drug development. Our extensive global network and unwavering commitment to providing novel solutions puts World Precision Instruments at the forefront of drug discovery today.
References
- Food and Drug Administration (Novel Drug Approvals for 2022 | FDA)
- Fierce Pharma (Top 10 most anticipated drug launches of 2023 (fiercepharma.com))
- American Society for Gene and Cell Therapy (asgct-pharma-intelligence-q1-2022-report.aspx)
- Reimagining patient-centric cancer clinical trials: a multi-stakeholder international coalition (Reimagining patient-centric cancer clinical trials: a multi-stakeholder international coalition | Nature Medicine)
- FDA Modernization Act 2.0 allows for alternatives to animal testing (FDA Modernization Act 2.0 allows for alternatives to animal testing - PubMed (nih.gov))

Close