This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
Read more
VIDEO: Comparison of Metal for Surgical Instruments
February 10, 2022
Surgical instruments are designed to perform diagnostic, therapeutic, or investigative operations having specific functions such as to cut or incise, retract, grasp, hold or occlude, dilate or probe, suture or ligate.
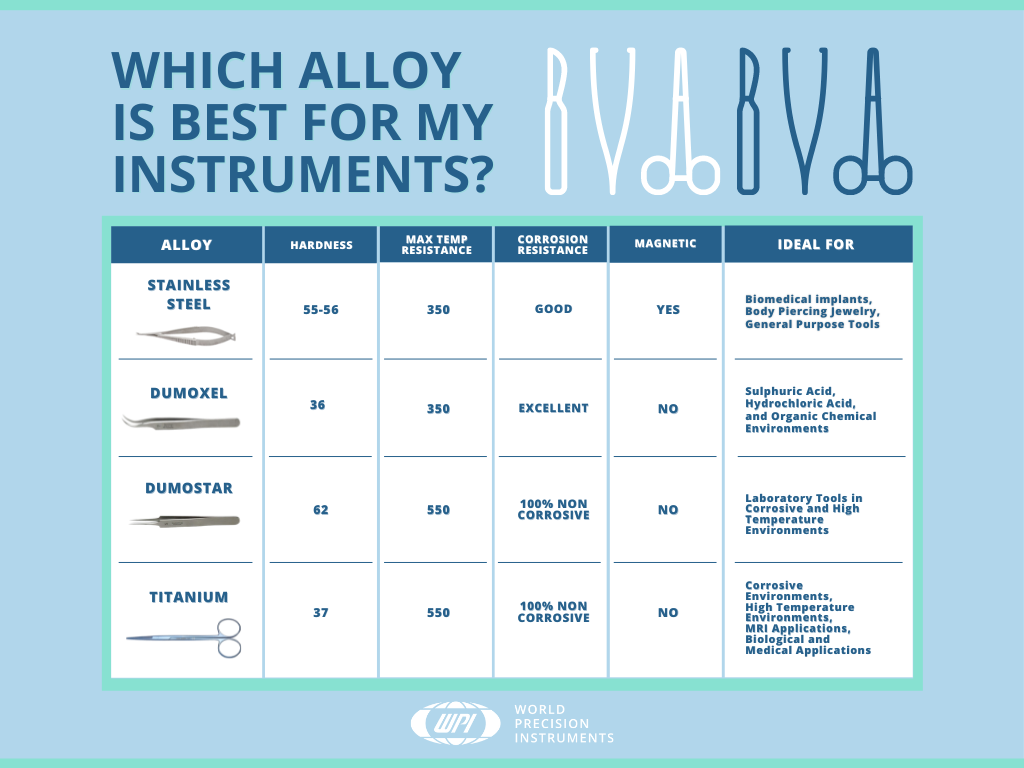
The majority of surgical instruments are made of stainless steel or titanium (used where non-magnetic instruments are required). Stainless steel is an alloy that contains a minimum 12% chromium for corrosion resistance. Here's a quick comparison chart looking a various metals used in surgical instruments and the best applications for each.
Stainless Steel
Austenitic 316 steel, also called surgical steel or marine grade steel is the most common alloy used for WPI's standard line of instruments. Surgical steel has excellen corrosion-resistance, which makes it a good choice for biomedical implants or body piercing jewelery, as well as surgical instruments. It is in compliance with ASTM F138. Stainless steel (Inox) also has good salt resistance and temperature resistant up to 400°C.
Dumoxel Steel
Dumont Tools developed several special types of stainless steel for their premium surgical instrument. Dumoxel is highly resistant to sulphuric environments, hydrochloric acid, mineral and organic acids. It is extremely flexible and 95% antimagnetic. Dumoxel resists stains. The high molybedum and chromium content increases its resistance to corrosion. It is more likely to bend than break. It is temperature resistant up to 400°C (autoclaved at 270°C). Dumoxel is the most popular Dumont alloy for tools.
Dumostar Steel
Dumont also patented Dumostar, which is more elastic and more corrosion-resistant than the best stainless steel. It is resistant to minerals, organic acids and salt corrosion. Dumostar is 100% anti-magnetic and temperature resistant up to 500°C. Because of its high resistant to metal fatigue, Dumostar steel has great elasticity and durability. Like Dumoxel, Dumostar is more likely to bend than break. Dumostar is the most cost-effective and appropriate alloy for laboratory tools.
Titanium
Titanium is non-ferous, making it 100% anti-magnetic. It is corrosion-resistant, lightweight and strong. These qualities make titanium alloys perfect for biological and medical applications. While titanium has the tensile strength of carbon steel, it is completely resistant to corrosion from nitric acid, chloride, saltwater, industrial chemicals and organic chemicals. Titanium is more flexible and 40% lighter than Inox stainless steel. The lighter weight of titanium instruments means you experience less hand fatigue when you are using them for long periods of time. When heated or cooled, the dimensions of titanium alloy change less than half of what stainless steel alloys will. Since most instruments are autoclaved repeated for sterilization purposes, this feature ensurs that your titanium surgical instruments will have a significantly longer life. The expansion and contraction of the metal causes fatigue and stresses the joints. Titanium is stain-free and temperature resistant up to 430°C. Titanium tools are the premium choice for corrosive environments and MRI applications.

Close