This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
Read more
Thin Wall Glass Capillaries
As low as
$70.00
Only %1 left
Prices valid in USA, Canada, and PR only.
Order code
Price range: $70 - $92

Prices valid in USA, Canada, and PR only.
Quality glass capillaries at superior prices for microinjection and microelelctrodes.
Prices valid in USA, Canada, and PR only.
Quality glass capillaries at superior prices for microinjection and microelelctrodes
Features
- Quality borosilicate glass capillaries
- Large variety available
- Some varieties of fire polished capillary glass(See description)
- OD/ID Tolerance: ±0.1 mm
- Length Tolerance: ±1 mm
- Recommended to use with Glass Handling Forceps (77020)
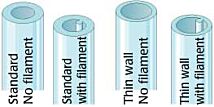
Thin-Wall Single-Barrel Standard Borosilicate (Schott Duran) Glass Tubing Options
| Order code | Length | OD (mm) | ID (mm) | Filament | Fire Polish | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TW100F-3 | 3 in. (76mm) | 1.0 | 0.75 | • | 500 | |
| TW100-3 | 3 in. (76mm) | 1.0 | 0.75 | 500 | ||
| TW120F-3 | 3 in. (76mm) | 1.2 | 0.90 | • | • | 400 |
| TW120-3 | 3 in. (76mm) | 1.2 | 0.90 | 350 | ||
| TW150F-3 | 3 in. (76mm) | 1.5 | 1.12 | • | 225 | |
| TW150-3 | 3 in. (76mm) | 1.5 | 1.12 | • | 300 | |
| TW100F-4 | 4 in. (100mm) | 1.0 | 0.75 | • | 500 | |
| TW100-4 | 4 in. (100mm) | 1.0 | 0.75 | • | 500 | |
| TW120F-4 | 4 in. (100mm) | 1.2 | 0.90 | • | 350 | |
| TW120-4 | 4 in. (100mm) | 1.2 | 0.90 | 350 | ||
| TW150F-4 | 4 in. (100mm) | 1.5 | 1.12 | • | 225 | |
| TW150-4 | 4 in. (100mm) | 1.5 | 1.12 | • | 300 | |
| TW100F-6 | 6 in. (152mm) | 1.0 | 0.75 | • | 500 | |
| TW100-6 | 6 in. (152mm) | 1.0 | 0.75 | • | 500 | |
| TW120F-6 | 6 in. (152mm) | 1.2 | 0.90 | • | • | 400 |
| TW120-6 | 6 in. (152mm) | 1.2 | 0.90 | 350 | ||
| TW150F-6 | 6 in. (152mm) | 1.5 | 1.12 | • | 225 | |
| TW150-6 | 6 in. (152mm) | 1.5 | 1.12 | • | 300 |
Benefits
- Superior pricing
- Most glass capillary orders ship within 48 hours
Applications
- Microinjection
- Electrophysiology
- Patch clamp
- Fluid Handling
Fire Polishing
Fire-Polished glass capillaries are easier to insert into microelectrode holders without damaging the gasket. More importantly, fire-polished glass capillaries won’t scratch the chloridized wire used in a recording electrode. Fire-polishing does not affect the glass’s mechanical or electrical properties.
Making Uniform, Reproducible Microelectrodes
Borosilicate glass capillaries: Close dimensional tolerances assure microelectrode uniformity and reproducibility. Glass capillaries are available in 1, 2, 3, 5 and 7-barrel configurations, complete range of single barrel thin-wall sizes and a variety of special configurations. Glass capillaries with filaments contain a solid filament fused to the inner wall, which speeds filling of electrodes. Glass capillaries with or without inner filaments are available for making microelectrodes in a wide range of diameters.
Capillary Glass with Filament
Single Barrel standard wall thickness glass capillaries are offered either with or without inner filaments for quick filling in a variety of lengths and diameters.
Thin Wall Glass Capillaries
Thin Wall single barrel glass capillaries are offered both with or without inner filaments.
NOTE: Because electrode tips erode when left filled with saline solutions for long periods, electrodes should be made and filled immediately prior to use.
More Information on Glass Capillary
Buying Multi-Barrel Glass Capillaries
Buying Capillaries for Making Micropipettes and Microelectrodes
| SKU | VAR-3709 |
|---|
Henao-Mejia, J., Williams, A., Rongvaux, A., Stein, J., Hughes, C., & Flavell, R. A. (2016). Generation of Genetically Modified Mice Using the CRISPR-Cas9 Genome-Editing System. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols, 2016(2), pdb.prot090704. http://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.prot090704
Xie, Y., Zhou, Y., Xi, W., Zeng, F., & Chen, S. (2016). Fabrication of a Cell Fixation Device for Robotic Cell Microinjection. Micromachines, 7(8), 131. http://doi.org/10.3390/mi7080131
Engerer, P., Plucinska, G., Thong, R., Trovò, L., Paquet, D., & Godinho, L. (2016). Imaging Subcellular Structures in the Living Zebrafish Embryo. Journal of Visualized Experiments, (110), e53456–e53456. http://doi.org/10.3791/53456
Vidal, G. S., Djurisic, M., Brown, K., Sapp, R. W., & Shatz, C. J. (2016). Cell-Autonomous Regulation of Dendritic Spine Density by PirB. eNeuro, 3(5). http://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0089-16.2016
Lai, J., Legault, M.-A., Thomas, S., & Casanova, C. (2015). Simultaneous Electrophysiological Recording and Micro-injections of Inhibitory Agents in the Rodent Brain. Journal of Visualized Experiments, (101), e52271–e52271. http://doi.org/10.3791/52271
Smith, S. J., Horstick, E. J., Davidson, A. E., & Dowling, J. (2015). Analysis of Zebrafish Larvae Skeletal Muscle Integrity with Evans Blue Dye. Journal of Visualized Experiments, (105), e53183–e53183. http://doi.org/10.3791/53183
Lundgaard, I., Li, B., Xie, L., Kang, H., Sanggaard, S., Haswell, J. D. R., … Nedergaard, M. (2015). Direct neuronal glucose uptake heralds activity-dependent increases in cerebral metabolism. Nature Communications, 6, 6807. http://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms7807
Deline, M., Keller, J., Rothe, M., Schunck, W.-H., Menzel, R., & Watts, J. L. (2015). Epoxides Derived from Dietary Dihomo-Gamma-Linolenic Acid Induce Germ Cell Death in C. elegans. Scientific Reports, 5, 15417. http://doi.org/10.1038/srep15417
Jarriault, D., & Grosmaitre, X. (2015). Perforated Patch-clamp Recording of Mouse Olfactory Sensory Neurons in Intact Neuroepithelium: Functional Analysis of Neurons Expressing an Identified Odorant Receptor. Journal of Visualized Experiments, (101), e52652–e52652. http://doi.org/10.3791/52652
Leslie, J. L., Huang, S., Opp, J. S., Nagy, M. S., Kobayashi, M., Young, V. B., & Spence, J. R. (2015). Persistence and toxin production by Clostridium difficile within human intestinal organoids result in disruption of epithelial paracellular barrier function. Infection and Immunity, 83(1), 138–45. http://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.02561-14
Konantz, J., & Antos, C. L. (2014). Reverse Genetic Morpholino Approach Using Cardiac Ventricular Injection to Transfect Multiple Difficult-to-target Tissues in the Zebrafish Larva. Journal of Visualized Experiments, (88), e51595–e51595. http://doi.org/10.3791/51595
Thomson, S. J., Hansen, A., & Sanguinetti, M. C. (2014). Concerted all-or-none subunit interactions mediate slow deactivation of human ether-à-go-go-related gene K+ channels. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 289(34), 23428–36. http://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.582437
Voigt, D., Konrad, W., & Gorb, S. (2014). A universal glue: underwater adhesion of the secretion of the carnivorous flypaper plant Roridula gorgonias. Interface Focus, 5(1).
Walton, K. D., & Kolterud, Å. (2014). Mouse Fetal Whole Intestine Culture System for <em>Ex Vivo</em> Manipulation of Signaling Pathways and Three-dimensional Live Imaging of Villus Development. Journal of Visualized Experiments, (91), e51817–e51817. http://doi.org/10.3791/51817
Harms, D. W., Quadros, R. M., Seruggia, D., Ohtsuka, M., Takahashi, G., Montoliu, L., & Gurumurthy, C. B. (2014). Mouse Genome Editing Using the CRISPR/Cas System. Current Protocols in Human Genetics, 83, 15.7.1-27. http://doi.org/10.1002/0471142905.hg1507s83
Wang, R., Palavicini, J. P., Wang, H., Maiti, P., Bianchi, E., Xu, S., … Lakshmana, M. K. (2014). RanBP9 overexpression accelerates loss of dendritic spines in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiology of Disease, 69, 169–79. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2014.05.029
Jang, J., Um, K. B., Jang, M., Kim, S. H., Cho, H., Chung, S., … Park, M. K. (2014). Balance between the proximal dendritic compartment and the soma determines spontaneous firing rate in midbrain dopamine neurons. The Journal of Physiology, 592(13), 2829–44. http://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2014.275032
Tonini, R., Ferraro, T., Sampedro-Castañeda, M., Cavaccini, A., Stocker, M., Richards, C. D., & Pedarzani, P. (2013). Small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels modulate action potential-induced Ca2+ transients in hippocampal neurons. Journal of Neurophysiology, 109(6), 1514–24. http://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00346.2012
Recording Pipettes. (2013). Cold Spring Harbor Protocols, 2013(2), pdb.rec073759-rec073759. http://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.rec073759
Yang, D., Zhang, J., Xu, J., Zhu, T., Fan, Y., Fan, J., & Chen, Y. E. (2013). Production of Apolipoprotein C-III Knockout Rabbits using Zinc Finger Nucleases. Journal of Visualized Experiments, (81), e50957–e50957. http://doi.org/10.3791/50957
Nemes, P., Rubakhin, S. S., Aerts, J. T., & Sweedler, J. V. (2013). Qualitative and quantitative metabolomic investigation of single neurons by capillary electrophoresis electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Nature Protocols, 8(4), 783–99. http://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2013.035
Johnston, L., Ball, R. E., Acuff, S., Gaudet, J., Sornborger, A., & Lauderdale, J. D. (2013). Electrophysiological Recording in the Brain of Intact Adult Zebrafish. Journal of Visualized Experiments, (81), e51065–e51065. http://doi.org/10.3791/51065
Layden, M. J., Röttinger, E., Wolenski, F. S., Gilmore, T. D., & Martindale, M. Q. (2013). Microinjection of mRNA or morpholinos for reverse genetic analysis in the starlet sea anemone, Nematostella vectensis. Nature Protocols, 8(5), 924–34. http://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2013.009
Cao, Y., Pan, Y., Huang, H., Jin, X., Levin, E. J., Kloss, B., & Zhou, M. (2013). Gating of the TrkH ion channel by its associated RCK protein TrkA. Nature, 496(7445), 317–22. http://doi.org/10.1038/nature12056
Raissig, M. T., Gagliardini, V., Jaenisch, J., Grossniklaus, U., & Baroux, C. (2013). Efficient and Rapid Isolation of Early-stage Embryos from <em>Arabidopsis thaliana</em> Seeds. Journal of Visualized Experiments, (76), e50371–e50371. http://doi.org/10.3791/50371
Alfaqeeh, S. A., & Tucker, A. S. (2013). The Slice Culture Method for Following Development of Tooth Germs In Explant Culture. Journal of Visualized Experiments, (81), e50824–e50824. http://doi.org/10.3791/50824
Ludwar, B. C., Evans, C. G., & Cropper, E. C. (2012). Monitoring changes in the intracellular calcium concentration and synaptic efficacy in the mollusc Aplysia. Journal of Visualized Experiments : JoVE, (65), e3907. http://doi.org/10.3791/3907
Luo, J., Yan, X., Lin, J., & Rolfs, A. (2012). Gene transfer into older chicken embryos by ex ovo electroporation. Journal of Visualized Experiments : JoVE, (65). http://doi.org/10.3791/4078
Yang, B., Geary, L. B., & Ma, Y.-C. (2012). No Title, (66). http://doi.org/10.3791/4017
Veeman, M. T., Chiba, S., & Smith, W. C. (2011). Ciona genetics. Methods in Molecular Biology (Clifton, N.J.), 770, 401–22. http://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-210-6_15
Kariu, T., Coleman, A. S., Anderson, J. F., & Pal, U. (2011). Methods for Rapid Transfer and Localization of Lyme Disease Pathogens Within the Tick Gut. Journal of Visualized Experiments, (48), e2544–e2544. http://doi.org/10.3791/2544
Gao, L., Kim, Y., Kim, B., Lofgren, S. M., Schultz-Norton, J. R., Nardulli, A. M., … Jorgensen, J. S. (2011). Two regions within the proximal steroidogenic factor 1 promoter drive somatic cell-specific activity in developing gonads of the female mouse. Biology of Reproduction, 84(3), 422–34. http://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod.110.084590
Staton, A. A., & Giraldez, A. J. (2011). Use of target protector morpholinos to analyze the physiological roles of specific miRNA-mRNA pairs in vivo. Nature Protocols, 6(12), 2035–49. http://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2011.423
Farah, C. A., & Sossin, W. S. (2011). No Title, (50), e2516–e2516. http://doi.org/10.3791/2516
Goldman, N., Chen, M., Fujita, T., Xu, Q., Peng, W., Liu, W., … Nedergaard, M. (2010). Adenosine A1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture. Nature Neuroscience, 13(7), 883–8. http://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2562
Shen, Z. L., Dodge, M. R., Kahn, H., Ballarini, R., & Eppell, S. J. (2010). In vitro fracture testing of submicron diameter collagen fibril specimens. Biophysical Journal, 99(6), 1986–95. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2010.07.021
Clemons, A., Haugen, M., Severson, D., & Duman-Scheel, M. (2010). Functional analysis of genes in Aedes aegypti embryos. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols, 2010(10), pdb.prot5511. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20889708
Stofanko, M., Kwon, S. Y., & Badenhorst, P. (2010). Lineage tracing of lamellocytes demonstrates Drosophila macrophage plasticity. PloS One, 5(11), e14051. http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0014051
Russek-Blum, N., Nabel-Rosen, H., & Levkowitz, G. (2010). Two-Photon-Based Photoactivation in Live Zebrafish Embryos. Journal of Visualized Experiments, (46), e1902–e1902. http://doi.org/10.3791/1902
Kumar, V., Alla, S. R., Krishnan, K. S., & Ramaswami, M. (2009). Syndapin is dispensable for synaptic vesicle endocytosis at the Drosophila larval neuromuscular junction. Molecular and Cellular Neurosciences, 40(2), 234–41. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2008.10.011
Wang, X., Takano, T., & Nedergaard, M. (2009). Astrocytic calcium signaling: mechanism and implications for functional brain imaging. Methods in Molecular Biology (Clifton, N.J.), 489, 93–109. http://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-543-5_5
Werren, J. H., Loehlin, D. W., & Giebel, J. D. (2009). Larval RNAi in Nasonia (parasitoid wasp). Cold Spring Harbor Protocols, 2009(10), pdb.prot5311. http://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.prot5311
Imlach, W., & McCabe, B. D. (2009). Electrophysiological Methods for Recording Synaptic Potentials from the NMJ of Drosophila Larvae. Journal of Visualized Experiments, (24), e1109–e1109. http://doi.org/10.3791/1109
Werren, J. H., & Loehlin, D. W. (2009). The parasitoid wasp Nasonia: an emerging model system with haploid male genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols, 2009(10), pdb.emo134. http://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.emo134
Chen, K., Augustin, H., & Featherstone, D. E. (2009). No Title, 195(1). http://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-008-0378-3
Stofanko, M., Kwon, S. Y., & Badenhorst, P. (2008). A misexpression screen to identify regulators of Drosophila larval hemocyte development. Genetics, 180(1), 253–67. http://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.108.089094
Luo, J., & Redies, C. (2005). Ex ovo electroporation for gene transfer into older chicken embryos. Developmental Dynamics, 233(4), 1470–1477. http://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.20454
Xi, Z., & Dobson, S. L. (2005). Characterization of Wolbachia transfection efficiency by using microinjection of embryonic cytoplasm and embryo homogenate. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71(6), 3199–204. http://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.6.3199-3204.2005
Jerng, H. H., Qian, Y., & Pfaffinger, P. J. (2004). Modulation of Kv4.2 channel expression and gating by dipeptidyl peptidase 10 (DPP10). Biophysical Journal, 87(4), 2380–96. http://doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.104.042358
Gómez-Viquez, L., Guerrero-Serna, G., García, U., & Guerrero-Hernández, A. (2003). SERCA pump optimizes Ca2+ release by a mechanism independent of store filling in smooth muscle cells. Biophysical Journal, 85(1), 370–80. http://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74481-6