This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
Read more
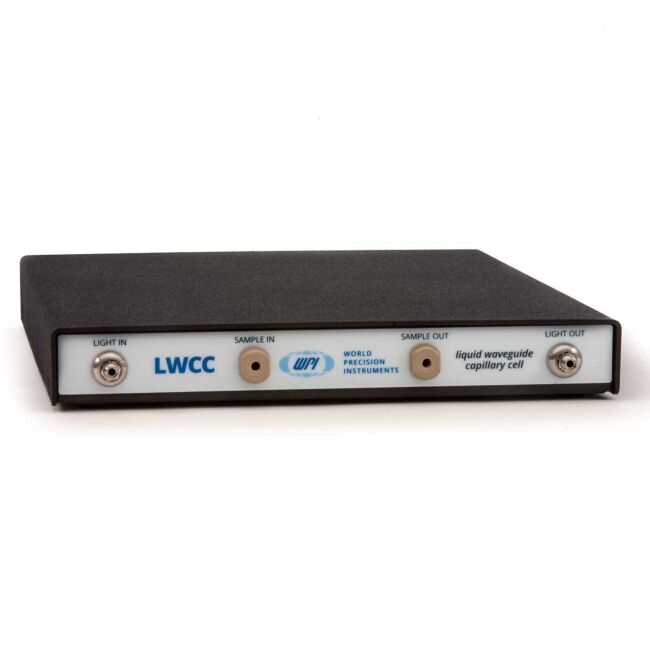
Liquid Waveguide Capillary Cell
As low as
$3,100.00
Only %1 left
Prices valid in USA, Canada, and PR only.
Order code
Price range: $3,100 - $4,100

Prices valid in USA, Canada, and PR only.
UV/VIS/NIR absorbance spectroscopy is governed by Beer’s Law, where the absorbance signal is proportional to chemical concentration, light path length and the compound’s specific molar absorption coefficient. Typical optical pathlengths of cuvettes and flow cells are between 0.2cm and 10 cm. Longer pathlengths are difficult to achieve due to mechanical constraints. Liquid Waveguide Capillary Cells (LWCCs) fill this gap. LWCCs are fiber optic flow cells that combine an increased optical pathlength (10–500 cm) with small sample volumes ranging from 2.4 µL to about 3mL. Compared with a standard 1cm cell, a 1 mAU signal is enhanced one hundred fold with a 100 cm flowcell to 100 mAU, using WPI’s patented aqueous waveguide technology.*
They can be connected via optical fibers to a spectrophotometer with fiber optic capabilities. Ultra-sensitive absorbance measurements can be performed in the ultraviolet (UV), visible (VIS) and near-infrared (NIR) to detect low sample concentrations in a laboratory or process control environment.
To learn more about our warranty options, click here.
Prices valid in USA, Canada, and PR only.
Microliter Sample Volume - Exceptional Sensitivity
Features
- Optical sample flow cell that combines an increased optical pathlength with a small sample volume.
- Measure liquids in a continuous flow or using discrete samples
- Connects with 600um core optical fibers to fiber optic spectrometers and light sources via SMA terminations
- Efficient measurement of low-volume or low-concentration (ppb-ppt) aqueous samples.
- Functions with most liquids(with the exception of perfluorinated solvents) having a refractive index ≥ 1.30
- Absorbance measurements can be performed in the UV, VIS, and NIR ranges to detect low sample concentrations in a lab or process environment.
Options
| Order code | Pathlength | Description |
| LWCC-3050 | 50cm Pathlength |
|
| LWCC-3100 | 100cm Pathlength |
|
| LWCC-3250 | 250cm Pathlength |
|
| LWCC-3500 | 500cm Pathlength |
|
Click here to view the current Data Sheet.
Benefits
- Adapts to most fiber optic detection systems via SMA terminations
- Efficient measurement of low-volume or low-concentration (ppb-ppt) aqueous samples
- Functions with most liquids (with the exception of perfluorinated solvents) having a refractive index ≥ 1.30
- Absorbance measurements can be performed in the UV, VIS, and NIR ranges
- 20 years of manufacturing experience
- Low UV drift
- Premium Warranty Available
The LWCC connects directly to a pump (e.g.WPI's MINISTAR), a chromatography column, a WPI Sample Injector Assembly (58006), Syringe Adapter Kit (58450), or the LWCC Injection System (89372)
Note: WPI offers the LWCC Start-up Kit (KITLWCC) includes two 1 meter fiber optic cables (505195), Sample Injector Assembly (58006) MiniStar™ Peristaltic Pump (MiniStar), and Waveguide Cleaning Kit (501609)
LWCC Properties
- Similar to optical fibers, light is confined with the (liquid) core of an LWCC by total internal reflection at the core/wall interface
- Made from fused silica tubing with an outer coating of a low refractive index polymer.
Pressure and Flow Rate
Flow is proportional to pressure and to the fourth power of the diameter of the fluid capillary, as well as the reciprocal to the length of the capillary and fluid viscosity
- 1 m of 55 μm ID waveguide requires approximately 1.5 PSI for water flow of 1mL/min
- LWCC has been operated at 100 to 200 PSI without observed malfunction
- Maximum hydrostatic pressure the LWCC can withstand has not been established
Applications
- Trace detection of nutrients (nitrite, nitrate, phosphate, iron) in seawater
- Environmental and oceanographic monitoring
- Drinking water analysis
- Colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM)
- Process control
Your sample is the core of a light guide
WPI’s Liquid Waveguide Capillary Cells are made of fused silica tubing with an outer coating of a low refractive index polymer. Your liquid sample is guided through the capillary and represents the core of the waveguide. The hydrophilic character of the fused silica capillary inner wall results in high signal stability and easy removal of air bubbles trapped in the flow cell. However, the transmission of the LWCC is mainly dependent on the intrinsic attenuation of the sample liquid.
Transmission into the NIR is possible when switiching water to methanol as a solvent.
Connections
The LWCC-3xxx series of flow cells uses traditional HPLC type 10-32 coned port fittings with 1/32 inch tubing for liquid connection and 500 µm SMA fiber optic adapters for light input and output. The LWCC-4xxx series of flow cells uses 1/4-28 flangless flat bottom fittings with 0.125" tubing 600 µm SMA fiber optic adapters.
Liquid can be pumped into the flow cells using (in the simplest case) either a sample injector (58006) or a ministar peristaltic pump (MINISTAR). The LWCC may be connected directly to a fluid injection analysis (FIA) system or to a gas segmented fluid injection analysis (GFIA) system via a debubbler.
For routing discrete measurements, WPI’s LWCC Injection system (89372) may be used when the sample is injected into a constant flow via an injection loop of 3–4 times the internal flow cell volume to ensure a stable baseline and avoid the introduction of micro air bubbles into the flow cell.
Example LWCC Measurement Setup and Order code
TIDAS E Photo Diode Array Spectrometer UV/VIS (504718)
Deuterium/Halogen Fiber Light Source (D4H)
Liquid Waveguide Capillary Cell, 50 cm pathlength(LWCC-3100)
*LWCC Start-up Kit (KITLWCC)
*includes two fiber cables(505195x2), sample injector attachement(58006), MiniStar Peristaltic Pump(MINISTAR) and Waveguide Cleaning Kit(501609).
Applications
LWCCs have been used in a variety of applications such as liquid chromatography, stopped-flow and colormetric detection, drinking water analysis, as well as environmental and oceanographic monitoring systems.
Related Patents
Micro Chemical Analysis Employing Flow Through Detectors, 1995, U.S. Patent No. 5,444,807.
Aqueous Fluid Core Waveguide, 1996, U.S. Patent No. 5,507,447.
Long Capillary Waveguide Raman Cell, 1997, U.S. Patent No. 5,604,587.
Chemical Sensing Techniques Employing Liquid-Core Optical Fibers, U.S. Patent No. 6,016,372
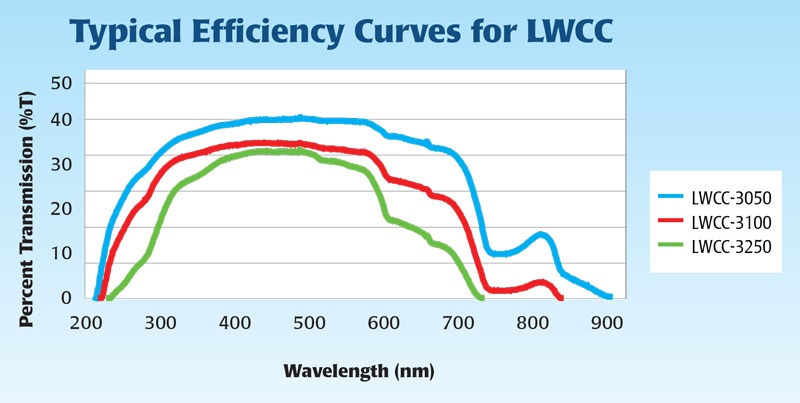
These spectra show the optimal detection limits for LWCCs of varying pathlength.
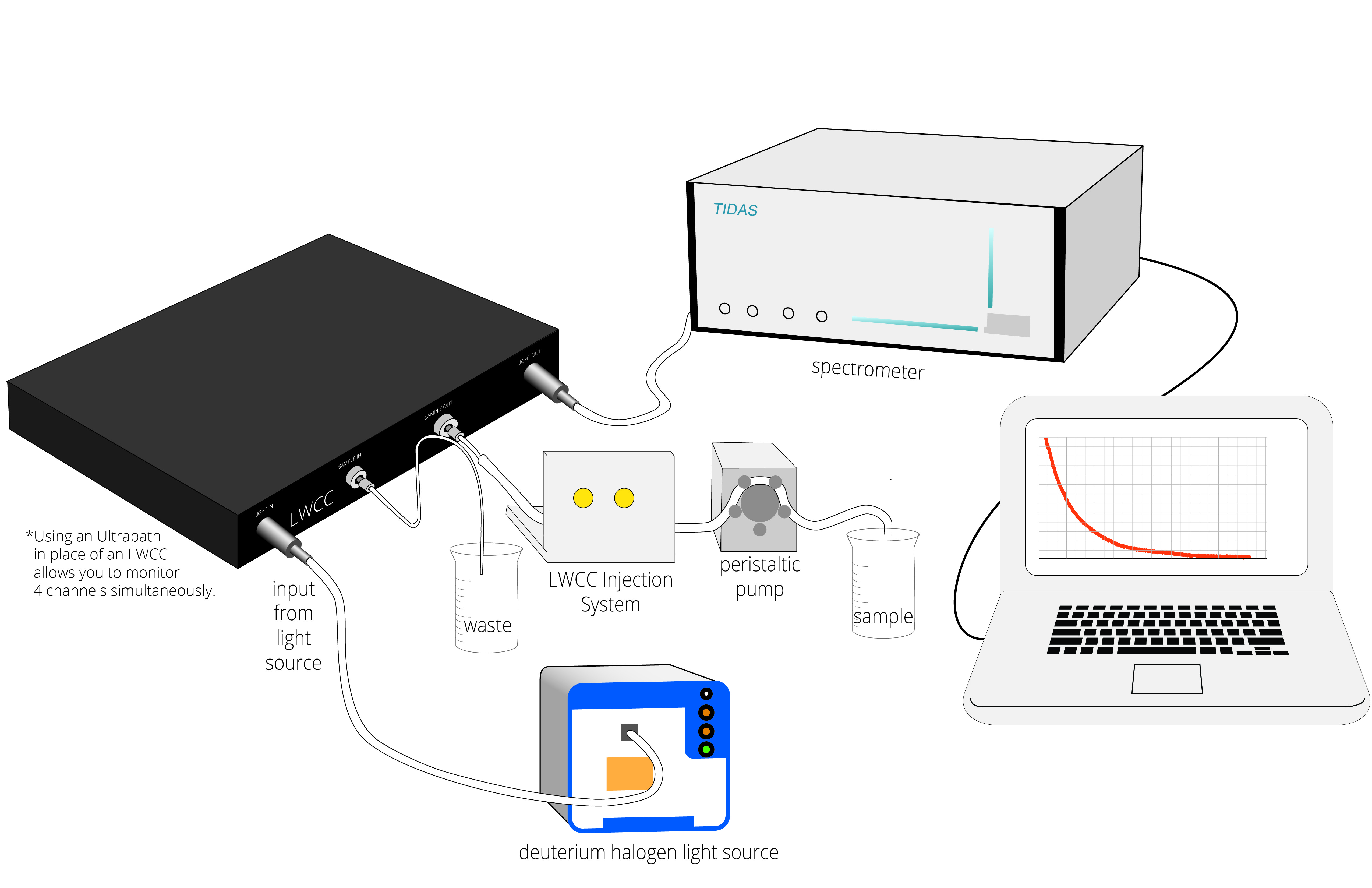
An illustration of a complete WPI long pathlength liquid absorbance system for trace detection.
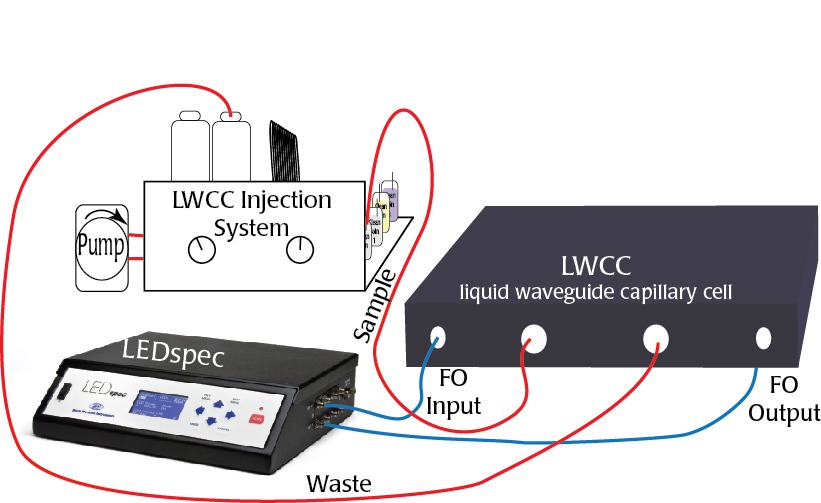
Typical LWCC setup includes an injection system, a pump, and a spectrophotometer.
| SKU | VAR-LWCC-3050 |
|---|
Upsell Products
Measure Colored Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM) Manual
Video
Long Pathlength Ensures Significant Increase of Sensitivity
| LWCC-3050 | LWCC-3100 | LWCC-3250 | LWCC-3500 | LWCC-4010 | LWCC-4050 | LWCC-4100 | |
| Optical Pathlength | 50 cm | 100 cm | 250 cm | 500 cm | 10 cm | 50 cm | 100 cm |
| Internal Volume | 125 µL | 250 µL | 625 µL | 1250 µL | 0.31 mL | 1.57 mL | 3.1 mL |
| Fiber Connection | 600 µm SMA | 600µm SMA | |||||
| Transmission @254nm* | ≥ 20 | ≥ 10 | ≥ 1 | - | ≥ 4 | ≥ 3 | ≥ 2 |
| Transmission @540nm* | ≥ 35 | ≥ 30 | ≥ 30 | ≥ 20 | ≥ 5 | ≥ 4 | ≥ 3 |
| Noise [mAU]** | <0.1 | <0.2 | <0.1 | <1.0 | <0.1 | <0.2 | <0.5 |
| Maximum Pressure | 100 PSI | ||||||
| Wetted Material | PEEK, Fused Silica, PTFE | ||||||
| Liquid Input | Standard 10-32 Coned Port Fitting | ||||||
* Referenced using coupled 500µm fibers
** Measured using ASTM E685-93
*** A one-meter waveguide of 550µm internal diameter requires approximately 1.5PSI for water flow of 1.0mL/min.
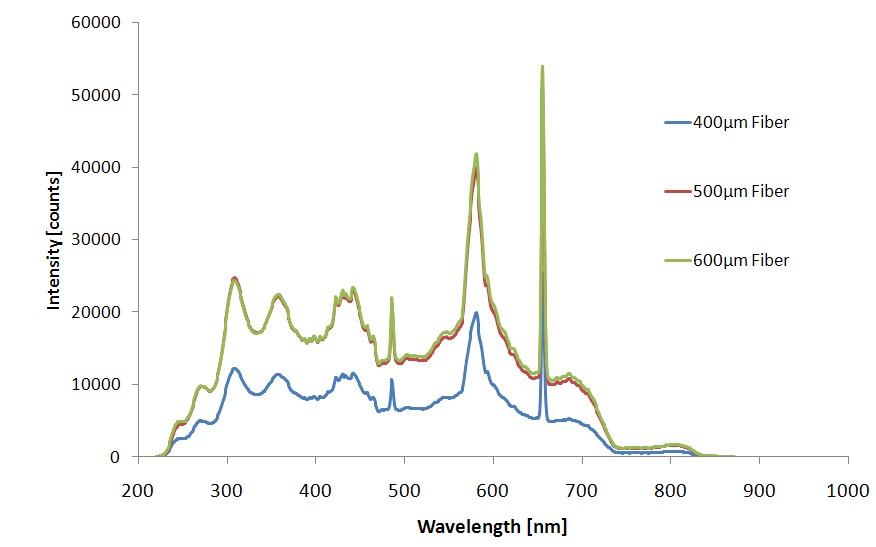
When comparing light throughput versus wavelength of three fiber optic cables, the greater the diameter of the cable, the better the LWCC performance up to 600µm which is the input diameter of the SMA connector.
Bregnhøj, M., McLoughlin, C. K., Breitenbach, T., & Ogilby, P. R. (2022). X 3 Σ g – → b 1 Σ g + Absorption Spectra of Molecular Oxygen in Liquid Organic Solvents at Atmospheric Pressure . The Journal of Physical Chemistry A. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpca.2c03053
Lefering, I., Röttgers, R., Utschig, C., & McKee, D. (2017). Uncertainty budgets for liquid waveguide CDOM absorption measurements. Applied Optics, 56(22), 6357. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.56.006357
Miranda, J. L. A., Mesquita, R. B. R., Nunes, A., Rangel, M., & Rangel, A. O. S. S. (2016). Iron speciation in natural waters by sequential injection analysis with a hexadentate 3-hydroxy-4-pyridinone chelator as chromogenic agent. Talanta, 148, 633–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.05.062
Ehama, M., Hashihama, F., Kinouchi, S., Kanda, J., & Saito, H. (2016). Sensitive determination of total particulate phosphorus and particulate inorganic phosphorus in seawater using liquid waveguide spectrophotometry. Talanta, 153, 66–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.02.058
Violaki, K., Fang, T., Mihalopoulos, N., Weber, R., & Nenes, A. (2016). Real-Time, Online Automated System for Measurement of Water-Soluble Reactive Phosphate Ions in Atmospheric Particles. Analytical Chemistry, 88(14), 7163–7170. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b01264
Ye, C., Zhou, X., Pu, D., Stutz, J., Festa, J., Spolaor, M., … Knote, C. (2016). Rapid cycling of reactive nitrogen in the marine boundary layer. Nature, 532(7600), 489–491. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature17195
Hashihama, F., Kanda, J., Tauchi, A., Kodama, T., Saito, H., & Furuya, K. (2015). Liquid waveguide spectrophotometric measurement of nanomolar ammonium in seawater based on the indophenol reaction with o -phenylphenol (OPP). Talanta, 143, 374–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.05.007
Wise, M., Shilling, J., Imholt, F., & Caylor, R. (2015). Determination of the Optical Properties of Secondary Organic Aerosol Particles. Faculty Research. Retrieved from https://commons.cu-portland.edu/msfacultyresearch/2
Wise, M. E., Shilling, J., Caylor, R., Wise, M. E. ;, & Shilling, J. ; (2015). Determination of Total Peroxide Content in Secondary Organic Aerosol Particles. Retrieved from http://commons.cu-portland.edu/msfacultyresearchhttp://commons.cu-portland.edu/msfacultyresearch/1
Huang, Y., Yuan, D., Zhu, Y., & Feng, S. (2015). Real-Time Redox Speciation of Iron in Estuarine and Coastal Surface Waters. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(6), 3619–3627. https://doi.org/10.1021/es505138f
Liu, Y., & Lu, K. (2015). In situ Monitoring of Atmospheric Nitrous Acid based on Multi-pumping flow system and Liquid Waveguide Capillary Cell: development and field applications. EGU General Assembly 2015, Held 12-17 April, 2015 in Vienna, Austria. Id.8298, 17.
Gil-Lozano, C., Losa-Adams, E., F.-Dávila, A., & Gago-Duport, L. (2014). Pyrite nanoparticles as a Fenton-like reagent for in situ remediation of organic pollutants. Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology, 5(1), 855–864. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.5.97
Ma, J., Yuan, D., & Byrne, R. H. (2014). Flow injection analysis of trace chromium (VI) in drinking water with a liquid waveguide capillary cell and spectrophotometric detection. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(1), 367–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3381-2
Imholt, F. (2014). Optical Properties of Secondary Organic Aerosols Using Ultraviolet/Visible Spectroscopy. Math & Science Department (SURI). Retrieved from https://commons.cu-portland.edu/suri_msd/13
Wise, M. E., Imholt, F., Caylor, R., Wise, M. E. ;, & Imholt, F. ; (2014). Composition and Optical Properties of Secondary Organic Aerosol Particles. Retrieved from http://commons.cu-portland.edu/mathscienceresearch/2
Catelani, T. A., Tóth, I. V., Lima, J. L. F. C., Pezza, L., & Pezza, H. R. (2014). A simple and rapid screening method for sulfonamides in honey using a flow injection system coupled to a liquid waveguide capillary cell. Talanta, 121, 281–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2013.12.034
Wise, M. E., Imholt, F., & Caylor, R. (2014). Composition and Optical Properties of Secondary Organic Aerosol Particles. Retrieved from http://commons.cu-portland.edu/mathscienceresearch
Milani, A. (2013). DEVELOPMENT OF MICROFLUIDIC TECHNOLOGY FOR IN-SITU DETERMINATION OF IRON AND MANGANESE IN NATURAL AQUATIC SYSTEMS. Retrieved from https://eprints.soton.ac.uk/365471/1/A%2520Milani_PhD%2520Thesis.pdf
Zhang, X., Lin, Y.-H., Surratt, J. D., & Weber, R. J. (2013). Sources, Composition and Absorption Ångström Exponent of Light-absorbing Organic Components in Aerosol Extracts from the Los Angeles Basin. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(8), 3685–3693. https://doi.org/10.1021/es305047b
Feng, S., Zhang, M., Huang, Y., Yuan, D., & Zhu, Y. (2013). Simultaneous determination of nanomolar nitrite and nitrate in seawater using reverse flow injection analysis coupled with a long path length liquid waveguide capillary cell. Talanta, 117, 456–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2013.09.042
Sánchez-Quiles, D., Tovar-Sánchez, A., & Horstkotte, B. (2013). Titanium determination by multisyringe flow injection analysis system and a liquid waveguide capillary cell in solid and liquid environmental samples. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 76(1–2), 89–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.09.024
Tóth, I. V, Santos, I. C., Azevedo, C. F. M., Fernandes, J. F. S., Páscoa, R. N. M. J., Mesquita, R. B. R., & Rangel, A. O. S. S. (2013). Flow-injection spectrophotometric determination of bromate in bottled drinking water samples using chlorpromazine reagent and a liquid waveguide capillary cell. Analytical Sciences : The International Journal of the Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry, 29(5), 563–570. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23665631
Zimmer, L. A., Cutter, G. A., & High, ". (2012). High Resolution Determination of Nanomolar Concentrations of Dissolved Reactive Phosphate in Ocean Surface Waters Using Long Path Liquid Waveguide Capillary Cells (LWCC) and Spectrometric Detection. OEAS Faculty Publications. Paper, 46. https://doi.org/10.4319/lom.2012.10.568
Bianchi, F., Dommen, J., Mathot, S., & Baltensperger, U. (2012). On-line determination of ammonia at low pptv mixing ratios in the CLOUD chamber. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 5(7), 1719–1725. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-5-1719-2012
Horstkotte, B., Alexovič, M., Maya, F., Duarte, C. M., Andruch, V., & Cerdá, V. (2012). Automatic determination of copper by in-syringe dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction of its bathocuproine-complex using long path-length spectrophotometric detection. Talanta, 99, 349–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2012.05.063
Nuno, R., De, M., & Páscoa, J. (2011). EXPLOITING THE USE OF A LIQUID WAVEGUIDE CAPILLARY CELL FOR SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC DETERMINATIONS IN FLOW-BASED SYSTEMS. Retrieved from https://search.proquest.com/openview/af6e8eef15339d85d69d9846a84d3dc1/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=2026366&diss=y
Páscoa, R. N. M. J., Tóth, I. V., & Rangel, A. O. S. S. (2011). Spectrophotometric determination of zinc and copper in a multi-syringe flow injection analysis system using a liquid waveguide capillary cell: Application to natural waters. Talanta, 84(5), 1267–1272. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TALANTA.2011.01.023
Zhang, X., Hecobian, A., Zheng, M., Frank, N. H., & Weber, R. J. (2010). Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Biomass burning impact on PM 2.5 over the southeastern US during 2007: integrating chemically speciated FRM filter measurements, MODIS fire counts and PMF analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys, 10, 6839–6853. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-10-6839-2010
Hecobian, A., Zhang, X., Zheng, M., Frank, N., Edgerton, E. S., & Weber, R. J. (2010). Water-Soluble Organic Aerosol material and the light-absorption characteristics of aqueous extracts measured over the Southeastern United States. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 10(13), 5965–5977. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-10-5965-2010
Müller, M., Acker, M., Taut, S., & Bernhard, G. (2010). Complex formation of trivalent americium with salicylic acid at very low concentrations. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 286(1), 175–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-010-0639-9
Heller, M. I., & Croot, P. L. (2010). Kinetics of superoxide reactions with dissolved organic matter in tropical Atlantic surface waters near Cape Verde (TENATSO). Journal of Geophysical Research, 115(C12), C12038. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JC006021
Hecobian, A., Zhang, X., Zheng, M., Frank, N., Edgerton, E. S., & Weber, R. J. (2010). Water-Soluble Organic Aerosol material and the light-absorption characteristics of aqueous extracts measured over the Southeastern United States. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 10, 5965–5977. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-10-5965-2010
Rastogi, N., Oakes, M. M., Schauer, J. J., Shafer, M. M., Majestic, B. J., & Weber, R. J. (2009). New technique for online measurement of water-soluble Fe(II) in atmospheric aerosols. Environmental Science & Technology, 43(7), 2425–2430. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19452896
Amornthammarong, N., & Zhang, J.-Z. (2009). Liquid-waveguide spectrophotometric measurement of low silicate in natural waters. Talanta, 79(3), 621–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2009.04.050
MA, J., YUAN, D., ZHANG, M., & LIANG, Y. (2009). Reverse flow injection analysis of nanomolar soluble reactive phosphorus in seawater with a long path length liquid waveguide capillary cell and spectrophotometric detection. Talanta, 78(1), 315–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2008.11.017
Gimbert, L. J., Haygarth, P. M., & Worsfold, P. J. (2007). Determination of nanomolar concentrations of phosphate in natural waters using flow injection with a long path length liquid waveguide capillary cell and solid-state spectrophotometric detection. Talanta, 71(4), 1624–1628. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TALANTA.2006.07.044
Belz, M. (2007). Simple and sensitive protein detection system using UV LEDs and liquid core waveguides. In T. Vo-Dinh, R. A. Lieberman, & G. Gauglitz (Eds.), Proceedings of SPIE (Vol. 6755, p. 675505). SPIE. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.735348
Gimbert, L. J., Haygarth, P. M., & Worsfold, P. J. (2007). Determination of nanomolar concentrations of phosphate in natural waters using flow injection with a long path length liquid waveguide capillary cell and solid-state spectrophotometric detection. Talanta, 71(4), 1624–1628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2006.07.044
Schofield, O., Kerfoot, J., Mahoney, K., Moline, M., Oliver, M., Lohrenz, S., & Kirkpatrick, G. (2006). Vertical migration of the toxic dinoflagellate Karenia brevis and the impact on ocean optical properties. Journal of Geophysical Research, 111(C6), C06009. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JC003115
Li, Q. P., Zhang, J.-Z., Millero, F. J., & Hansell, D. A. (2005). Continuous colorimetric determination of trace ammonium in seawater with a long-path liquid waveguide capillary cell. Marine Chemistry, 96(1–2), 73–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2004.12.001
Nozière, B. (2005). Organic reactions increasing the absorption index of atmospheric sulfuric acid aerosols. Geophysical Research Letters, 32(3), L03812. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL021942
Schofield, O., Bergmann, T., Oliver, M. J., Irwin, A., Kirkpatrick, G., Bissett, W. P., … Orrico, C. (2004). Inversion of spectral absorption in the optically complex coastal waters of the Mid-Atlantic Bight. Journal of Geophysical Research, 109(C12), C12S04. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003JC002071
United States. National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Office of Aero-Space Technology. (2002). Spinoff 2002. U.S. G.P.O.
Zhelyaskov, V. R., Liu, S., & Broderick, M. P. (2000). Analysis of nanoliter samples of electrolytes using a flow-through microfluorometer. Kidney International, 57(4), 1764–1769. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.2000.00022.x
Calderilla, C., Avivar, J., Leal, L. O., & Cerdà, V. (n.d.). Multivariate optimisation of a rapid and simple automated method for bismuth determination in well water samples exploiting long path length spectrophotometry. Retrieved from https://cimav.repositorioinstitucional.mx/1
full-text. (n.d.).
Issues in Global Environment: Freshwater and Marine Environments: 2011 Edition - Google Books. (n.d.). Retrieved January 28, 2019, from https://books.google.com/books?id=0_TBHvAwl1kC&pg=PA320&lpg=PA320&dq=iron+detection+using+LWCC&source=bl&ots=ugTI2IUyfz&sig=ACfU3U136w2VXDXuNwJ075 5WkGgASI4mAg&hl=en&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjJ3_NkJHgAhXqUd8KHWp6AzM4FBDoATACegQIBBAB#v=onepage&q=iron detection
ScienceDirect (Online service). (n.d.). Talanta. Elsevier.
full-text. (n.d.).
Chen, Y., Huang, Y., Feng, S., & Yuan, D. (n.d.). Please do not adjust margins Solid phase extraction coupled with a liquid waveguide capillary cell for simultaneous redox speciation analysis of dissolved iron in estuarine and coastal waters. Anal. Methods, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1039/x0xx00000x
Cho, H. R., Jung, E. C., Park, K. K., Park, Y. J., & Kim, W. H. (n.d.). Speciation of U(VI) Using a 1.0-meter Liquid Waveguide Capillary Cell. Retrieved from https://inis.iaea.org/search/search.aspx?orig_q=RN:38049243
Self referencing LED detection system for spectroscopy applications. (n.d.).
Imholt, F. (n.d.). Optical properties of secondary organic aerosols using ultraviolet/visible spectroscopy.
Cruise report 64PE370 on RV Pelagia. (n.d.).